Continuous Integration vs. Continuous Deployment

In the fast-paced world of software development, quality software delivery is critical. Continuous Integration (CI) along with Continuous Deployment (CD) are two practices towards this goal. While often referred to as CI/CD, they have different purposes and distinct benefits. In this article, we’ll discuss Continuous Integration vs. Continuous Deployment, how to implement CI / CD in development workflows and popular CI / CD tools and platforms reviewed.
Table of Contents
- Overview of CI/CD Practices
- Continuous Integration vs. Continuous Deployment: Key Differences
- Continuous Integration vs. Continuous Deployment: Benefits of Implementing in Development Workflows
- Popular CI/CD Tools and Platforms
- Conclusion
Overview of CI/CD Practices
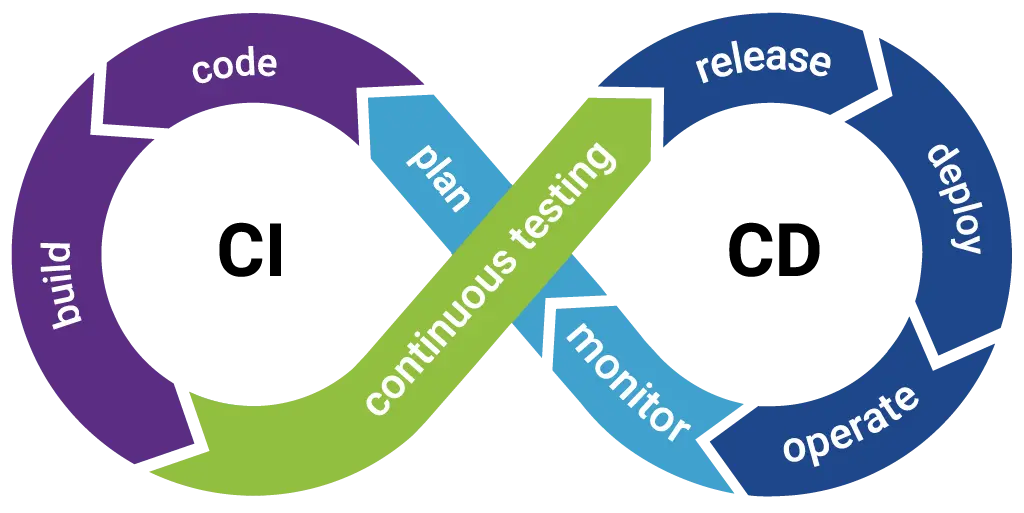
Continuous Integration (CI)
Continuous Integration is a software development technique where developers often push code changes into a distributed repository. Each integration is verified with automated tests to ensure a stable codebase without bugs. The main objective of CI is detecting early integration issues and to prevent major issues in the future.
Key Practices in CI
- Frequent Commits: Developers commit code changes frequently, often multiple times a day.
- Automated Testing: Automated tests are run on each integration to detect and fix bugs early.
- Build Automation: Automated build tools compile the code and generate executable files.
- Feedback Loop: Developers receive immediate feedback on the status of their integration, allowing them to address issues quickly.
Continuous Deployment (CD)
Continuous Deployment extends the principles of Continuous Integration by automatically deploying every code change that passes the automated tests to production. This practice makes the latest version of the software always available to users, encouraging rapid and reliable releases.
Key Practices in CD
- Automated Deployment: Code changes are automatically deployed to production without manual intervention.
- Release Automation: Automated tools handle the entire release process, from building to deploying the software.
- Monitoring and Alerts: Continuous monitoring ensures the software is performing as expected, and alerts notify developers of any issues.
- Rollback Mechanisms: Automated rollback mechanisms are in place to revert to a previous version if a deployment causes problems.
Continuous Integration vs. Continuous Deployment: Key Differences
While CI and CD are closely related, they serve different purposes and involve distinct processes.
Purpose
- CI: The main goal of CI is to detect and fix integration issues early by integrating code changes frequently and running automated tests.
- CD: The primary aim of CD is to automate the deployment process, ensuring that every code change that passes tests is automatically deployed to production.
Process
- CI: Involves frequent code commits, automated testing, and build automation. The focus is on integrating code changes into a shared repository.
- CD: Builds on CI by adding automated deployment and release processes. The focus is on delivering software to production quickly and reliably.
Frequency
- CI: Code changes are integrated and tested frequently, often multiple times a day.
- CD: Deployments to production occur as often as code changes pass the automated tests, potentially multiple times a day.
Feedback
- CI: Provides immediate feedback to developers on the status of their integrations, helping them address issues quickly.
- CD: Provides continuous feedback on the health and performance of the software in production, ensuring that any issues are identified and resolved promptly.
Continuous Integration vs. Continuous Deployment: Benefits of Implementing in Development Workflows
Implementing CI/CD in development workflows offers numerous benefits, enhancing the efficiency, reliability, and quality of software delivery. To learn more about these sort of advancements, read more on DesignRush.
Faster Time to Market
CI/CD practices enable faster and more frequent releases, enabling businesses to bring new features and updates to market quickly. This agility allows organizations to be competitive and respond to customer demands quickly.
Improved Code Quality
Automated testing in CI tests code changes before integration to reduce the risk of bugs and errors. CD further improves code quality by deploying only the changes that pass all tests, so only stable and reliable code reaches production.
Reduced Integration Issues
Frequent integration in CI identifies and resolves integration issues before they become serious problems. This proactive approach minimizes disruptions and ensures a smoother development process.
Enhanced Collaboration
Frequent code commits and integrations encourage CI/CD to encourage greater collaboration between development teams. Automated feedback loops and shared repositories foster transparency and accountability among team members.
Increased Deployment Frequency
With CD, deployments are routine and automated, allowing more frequent releases. This on-going delivery of updates and new features increases user satisfaction and keeps the software current and relevant.
Greater Reliability
Automated testing and deployment processes remove human error risk from software releases. Monitoring and rollback in CD further improve reliability by ensuring that production issues are resolved quickly.
Scalability
CI/CD practices are scalable and can be applied to any size project. Growing development teams and more complex projects require CI/CD to provide a solid foundation for managing and delivering software.
Popular CI/CD Tools and Platforms
Several tools and platforms are available to help implement CI/CD practices. Here are some of the most popular ones:
Jenkins
Jenkins is an open-source automation server widely used for CI/CD. It supports a wide range of plugins, making it highly customizable and adaptable to various workflows.
Key Features
- Extensive plugin ecosystem
- Supports distributed builds
- Robust pipeline support
- Strong community support
GitLab CI/CD
GitLab CI/CD is integrated with the GitLab repository management platform, providing a seamless experience for managing code, running tests, and deploying applications.
Key Features
- Integrated with GitLab
- Supports Docker containers
- Easy configuration with
.gitlab-ci.yml - Comprehensive monitoring and analytics
Travis CI
Travis CI is a cloud-based CI/CD service that integrates with GitHub repositories. It is known for its simplicity and ease of use.
Key Features
- Simple configuration with
.travis.yml - Integration with GitHub
- Supports multiple languages and platforms
- Free for open-source projects
CircleCI
CircleCI is a cloud-native CI/CD platform that supports fast and scalable builds. It offers robust features for managing complex workflows.
Key Features
- Cloud-native with fast builds
- Supports Docker and Kubernetes
- Flexible configuration with
circle.yml - Insights and analytics for performance monitoring
Azure DevOps
Azure DevOps provides a suite of tools for CI/CD, including Azure Pipelines for automated builds and deployments. It integrates well with other Azure services.
Key Features
- Comprehensive suite of DevOps tools
- Integration with Azure services
- Supports multiple languages and platforms
- Advanced reporting and analytics
GitHub Actions
GitHub Actions is a CI/CD tool integrated with GitHub, allowing developers to automate workflows directly from their repositories.
Key Features
- Integrated with GitHub
- Easy configuration with YAML files
- Supports a wide range of actions and workflows
- Community-contributed actions and templates
Looking to enhance your team with top talent? Hire software developers through WireFuture for expert solutions and exceptional service. Discover more on our website!
Conclusion
Continuous Integration along with Continuous Deployment are practices that modern software developers implement to deliver software more often, a lot more reliably and with better quality. Whereas CI integrates code changes frequently and runs automated tests, CD automates the deployment process. Implementing CI/CD in development workflows leads to faster time to market, improved code quality, reduced integration issues and improved collaboration.
Making use of well known CI / CD programs and platforms like Jenkins, GitLab CI / CD, Travis CI, CircleCI, Azure DevOps and GitHub Actions, development teams can hasten the delivery of a program. Accepting CI/CD practices is an important way to keep up with the evolving software demands.
For more information and detailed guides on CI/CD implementation see the official documentation of the above mentioned tools and platforms.
Success in the digital age requires strategy, and that's WireFuture's forte. We engineer software solutions that align with your business goals, driving growth and innovation.
No commitment required. Whether you’re a charity, business, start-up or you just have an idea – we’re happy to talk through your project.
Embrace a worry-free experience as we proactively update, secure, and optimize your software, enabling you to focus on what matters most – driving innovation and achieving your business goals.




